Understanding Inguinal Hernia: Symptoms, Complications, and Treatment Options | Bariatric Surgery Mexico
Inguinal hernias are a common medical condition where a part of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, usually at the lower level of the abdomen. This condition accounts for about 75% of hernias, predominantly affecting the small intestine. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms, understand the potential complications, and explore the effective treatment options available, particularly laparoscopic surgery.
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine pushes through a weakened area in the lower abdominal muscles, creating a noticeable bulge. Inguinal and femoral hernias are types of hernias that can occur in the groin area. This bulge may become more apparent when standing, coughing, or performing physical activities and often reduces when lying down. If the protruding intestine can’t return to the abdominal cavity, it may become trapped, leading to a condition known as an “incarcerated hernia.” Further complications can arise if the blood supply to the trapped intestine is cut off, resulting in a “strangulated hernia,” a serious medical emergency requiring immediate surgical intervention.
An inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine pushes through a weakened area in the lower abdominal muscles, creating a noticeable bulge. This bulge may become more apparent when standing, coughing, or performing physical activities and often reduces when lying down. If the protruding intestine can’t return to the abdominal cavity, it may become trapped, leading to a condition known as an “incarcerated hernia.” Further complications can arise if the blood supply to the trapped intestine is cut off, resulting in a “strangulated hernia,” a serious medical emergency requiring immediate surgical intervention.
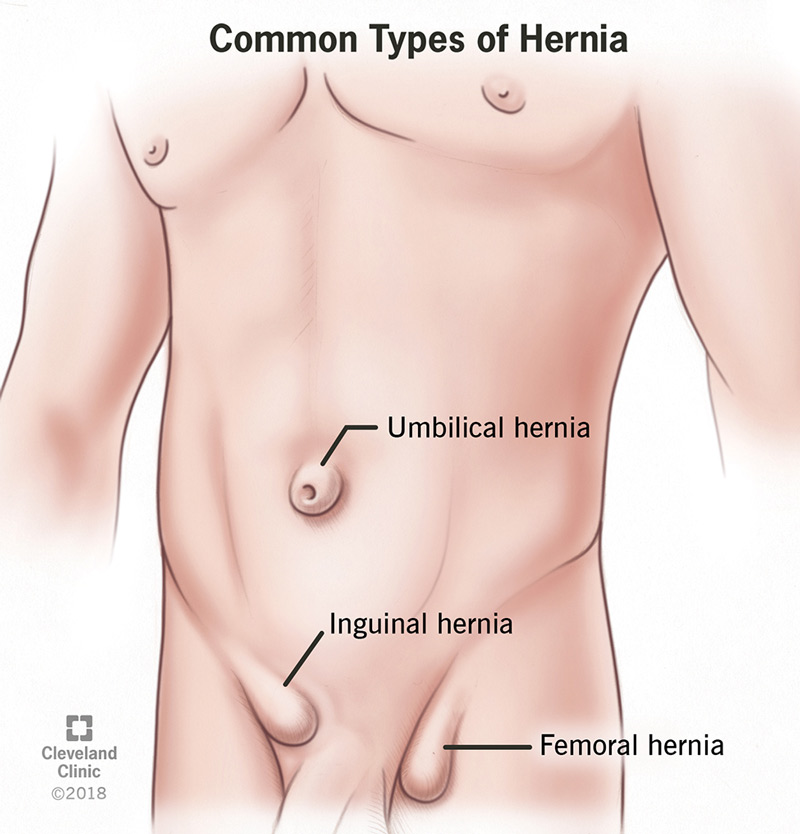
Type of hernias
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia, accounting for about 70% of all hernias. They occur when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles in the groin area. There are two types of inguinal hernias: indirect and direct.
Indirect inguinal hernias occur when the inguinal canal, a passage through the lower abdominal wall, doesn’t fully close during fetal development, allowing tissue to poke through. This type of hernia is more common in men and can occur at any age.
Direct inguinal hernias occur when abdominal tissues poke out through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, usually in the inguinal canal. This type of hernia is more common in older adults and can be caused by a weakening of the abdominal wall over time.
Femoral hernias, on the other hand, occur when tissue bulges through the lower belly and into the upper thigh, in the area just below the groin crease. They are relatively uncommon, making up fewer than 5% of all hernias, and are more common in women than in men.
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs of Inguinal Hernias
Symptoms of inguinal hernias can vary but typically include a visible bulge in the groin area, discomfort or pain during physical activities, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin. Men might experience swelling around the testicles if the protruding intestine descends into the scrotum. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms, especially if pain intensifies, as this could indicate complications such as incarceration or strangulation. Severe pain in the groin or abdomen can indicate serious complications and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of inguinal hernias can vary but typically include a visible bulge in the groin area, discomfort or pain during physical activities, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin. Men might experience swelling around the testicles if the protruding intestine descends into the scrotum. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms, especially if pain intensifies, as this could indicate complications such as incarceration or strangulation.
Complications of Untreated Inguinal Hernias: Strangulated Hernia
Symptoms of inguinal hernias can vary but typically include a visible bulge in the groin area, discomfort or pain during physical activities, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin. Men might experience swelling around the testicles if the protruding intestine descends into the scrotum. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms, especially if pain intensifies, as this could indicate complications such as incarceration or strangulation. Additionally, a femoral hernia, although less common, can also lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of inguinal hernias can vary but typically include a visible bulge in the groin area, discomfort or pain during physical activities, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin. Men might experience swelling around the testicles if the protruding intestine descends into the scrotum. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms, especially if pain intensifies, as this could indicate complications such as incarceration or strangulation.
Complications of Untreated Inguinal Hernias
Inguinal hernias, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications. An incarcerated hernia occurs when the herniated tissue becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. This can lead to bowel obstruction, causing nausea, vomiting, and severe abdominal pain. Strangulated hernias are even more critical as they cut off blood supply to the trapped intestine, leading to tissue death. This condition requires emergency surgery to prevent life-threatening consequences.
Diagnosing Inguinal Hernias
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who may ask the patient to cough or strain while standing to observe the hernia. Diagnosing an indirect inguinal hernia may involve specific imaging tests to confirm the condition. Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI might be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the hernia’s extent.
Treatment Options for Inguinal Hernias
Surgical intervention, often referred to as hernia surgery, is the primary treatment for inguinal hernias. Hernia repairs can vary in approach, including open and minimally invasive techniques. While watchful waiting might be recommended for asymptomatic hernias, surgery is advised for symptomatic cases or complications. The two main types of surgical repairs are open hernia repair and laparoscopic hernia repair.
Open Hernia Repair:
Open inguinal hernia repair involves a single, larger incision over the hernia site. The surgeon pushes the protruding intestine back into place and repairs the weakened area of the abdominal wall with stitches or synthetic mesh. Recovery time can be longer compared to laparoscopic methods.
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: A Minimally Invasive Hernia Repair
This minimally invasive technique involves several small incisions through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon uses a camera to guide the instruments and perform the hernia repair in Mexico with synthetic mesh. Opting for hernia repair in Mexico offers benefits such as shorter recovery time, less postoperative pain, and minimal scarring. Many patients choose hernia repair in Mexico due to the high-quality medical services and experienced surgeons available.
Recovery and Follow-up
After hernia repair surgery, patients can expect to experience some discomfort, swelling, and bruising in the groin area. The recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and the individual’s overall health.
For open hernia repair, patients may need to stay in the hospital for a few days and can expect to take several weeks to recover. For minimally invasive hernia repair, patients can usually go home the same day and can expect to recover within a few days to a week.
It’s essential to follow the surgeon’s instructions for post-operative care, including:
Resting and avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or straining
Taking pain medication as directed
Keeping the wound clean and dry
Attending follow-up appointments with the surgeon
Patients should also be aware of the signs of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or reaction to anesthesia, and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Prevention
The laparoscopic approach offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. These include:
- Shorter Recovery Time: Patients can often return to their normal activities within a few days.
- Reduced Postoperative Pain: Smaller incisions lead to less pain and discomfort post-surgery.
- Minimal Scarring: The small incisions result in less visible scars.
- Lower Recurrence Rate: The use of synthetic mesh and precise repair techniques lower the risk of hernia recurrence.
When is
While some hernias cannot be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing an inguinal hernia:
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the abdominal muscles
Exercising regularly to strengthen the abdominal muscles
Avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or straining
Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of chronic coughing
Eating a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and straining during bowel movements
It’s also essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of a hernia occur, as early treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernias are a common but manageable condition with effective treatment options available. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking medical evaluation can prevent complications. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair stands out as a highly successful and minimally invasive surgical option, offering rapid recovery and excellent outcomes. By understanding the condition and its treatments, patients can make informed decisions and ensure a swift return to their daily lives.
FAQS
Early signs include a visible bulge in the groin area, discomfort or pain during physical activities, and a heavy sensation in the groin.
Inguinal hernias do not heal on their own and typically require surgical intervention, especially if symptoms are present.
Untreated inguinal hernias can lead to incarceration and strangulation, causing bowel obstruction and tissue death, which require emergency surgery.
Risks include infection, bleeding, and complications related to anesthesia, similar to those associated with any surgical procedure
Laparoscopic surgery is suitable for most inguinal hernias, especially first-time repairs, recurrent hernias, and patients requiring a quick recovery.
